Human Lead AI - Rather than AI first
As businesses are racing to be “AI First,” I am advocating a Human Lead world of technology. How does this look in practice?
The "Human Led" AI Audit Checklist by Olivia Heslinga with links to extensive guides to implement each key step :
1. Scoping & Pre-Development
☐ Identify the "Invisible Stakeholders": Have you mapped out the groups most likely to be negatively impacted (e.g., gender, race, disability status)?
☐ Define the "Right to Recourse": If the AI makes a biased decision, is there a clear, human-led path for the user to appeal?
☐ Justification of Use: Can you articulate why an AI solution is safer or more equitable than a human process for this specific task?
Sources:
STAIR method (Sociotechnical AI Reflection): a leadership-oriented methodology for enabling responsible and participatory integration of Generative AI (GenAI) in organizational settings.
The Open Ethics Canvas is a tool for developers, product owners, and ethics professionals. Use it as a conversation starter in the process of building transparent and explainable technology products.
Training:
IBM: Reducing Unfair Bias in Machine Learning course
Link: https://www.ibm.com/training/course/reducing-unfair-bias-in-machine-learning-W7109G
Partnerships on AI: Job Impact Assessment
The Open Ethics Canvas v. 1
2. Data Integrity & Representation
☐ Audit the Training Data: Does the dataset reflect the diversity of the current population, or is it relying on historical data that mirrors past systemic biases?
☐ Labeling Transparency: Who labeled the data? If the labelers lack diversity or cultural context, bias may be "baked in" before the model is even trained.
☐ Synthetic Data Check: If using synthetic data to fill gaps, have you verified that it isn't simply hallucinating or reinforcing stereotypes?
Sources:
ITS Rio Technodiversity: Using technodiversity as a philosophical catalyst, our goal is to explore multifaceted forms of thinking about different technologies from the diverse socio-cultural contexts from which they emerge, rather than adhering to an all-encompassing "universal history."
Mohammad Atari, Mona J. Xue, Peter S. Park, Damián Blasi,Joseph Henrich. Which Humans? PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/5b26t
F. Clancy, R., Zhu, Q. & Majumdar, S. Exploring AI ethics in global contexts: a culturally responsive, psychologically realist approach. AI Ethics 5, 6329–6338 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-025-00821-6
Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43681-025-00821-6
Open Ethics Transparency Protocol: describes the creation and exchange of voluntary ethics Disclosures for products that involve Automated Decision-Making (ADM), including AI-powered services, Robotic process automation (RPA) tools, and robots.
Link : https://openethics.ai/oetp
Training:
University of Helsinki: Ethics of AI - Who should be blamed
Link: https://ethics-of-ai.mooc.fi/chapter-3/1-algorithms-and-accountability
AI Standards Hub: Assessing and mitigating bias and discrimination in AI
Link: https://aistandardshub.org/the-ai-standards-hub
Tools:
Google SynthID: A tool to watermark and identify content generated through (Google) AI
Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity, or C2PA, provides an open technical standard for publishers, creators and consumers to establish the origin and edits of digital content.
Link: https://c2pa.org
C2PA Content Credentials function like a nutrition label for digital content, giving a peek at the content’s history available for anyone to access, at any time.
3. Model Performance & Equity Testing
☐ Disparate Impact Analysis: Does the model’s error rate vary significantly across different demographic groups?
☐ The "Red-Teaming" Phase: Have you employed "data activists" or external DEIB experts to intentionally try to "break" the system or trigger biased outputs?
☐ Contextual Accuracy: Does the AI understand cultural nuances (e.g., African American Vernacular English or regional dialects) or does it flag them as "low quality"?
Sources
Eticas: Bias & Audit Framework An open-source Python library designed for developers to calculate fairness metrics and assess bias in machine learning models
Google Know your Data: helps researchers, engineers, product teams, and decision makers understand datasets with the goal of improving data quality, and helping mitigate fairness and bias issues.
Link: https://knowyourdata.withgoogle.com/
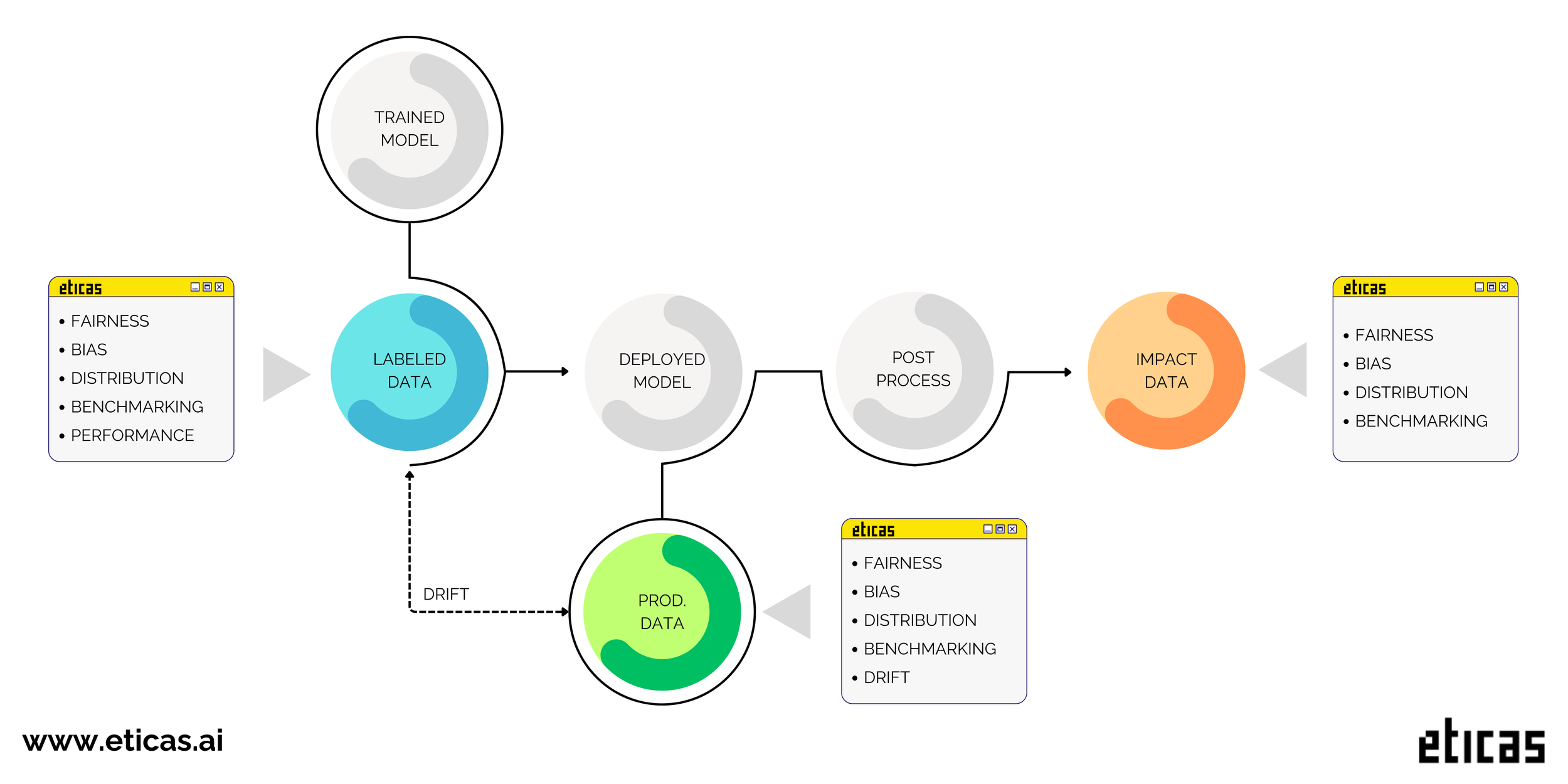
4. Post-Deployment & Governance
☐ Continuous Feedback Loops: Is there a mechanism for users to report bias in real-time?
☐ Algorithmic Drift Monitoring: Are you scheduled to re-audit every 3–6 months to ensure the AI hasn't developed new biases as it processes more live data?
☐ Kill-Switch Protocol: Is there a clear threshold of bias at which the organization is committed to taking the system offline?
Sources:
Marino, Bill & Aleksandrov, Preslav & Rahman, Carwyn & Pi, Yulu & Shen, Bill & Yew, Rui-jie & Lane, Nicholas. (2024). Compliance Cards: Computational Artifacts for Automated AI Regulation Compliance. 10.48550/arXiv.2406.14758.
Generative AI Playbook (Colorado University) : aims to assist practitioners in diagnosing potential harms that may arise during the design, development, and deployment of datasets and models.
Link: AI for Good Denmark : Reports
I hope this short list gives you some inspiration on how your organization, government and institution can start this important discussion when designing, building, implementing and monitoring AI systems.
This is not an extensive list of potential problems, risks, and cybersecurity issues that can be compounded with AI integration, overreliance, underfitting and overfitting the models in its context. Understanding both the business and human application is needed for strategic alignment and oversight.